Difference between revisions of "Clitoris"
(created) |
m (fixed REF issue; moved 2nd photo downwards) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Clitoris Anatomy.svg|thumb|The internal anatomy of the human [[vulva]], with the [[clitoral hood]] and [[labia minora]] indicated as lines. The clitoris extends from the visible portion to a point below the pubic bone.]] | [[File:Clitoris Anatomy.svg|thumb|The internal anatomy of the human [[vulva]], with the [[clitoral hood]] and [[labia minora]] indicated as lines. The clitoris extends from the visible portion to a point below the pubic bone.]] | ||
| − | |||
The '''clitoris''' is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the [[labia minora]] (inner lips), above the opening of the [[urethra]]. Unlike the [[penis]], the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris.<ref name=WP>{{URLwikipedia|Clitoris|Clitoris|2021-11-24}}</ref><ref>{{REFbook | The '''clitoris''' is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the [[labia minora]] (inner lips), above the opening of the [[urethra]]. Unlike the [[penis]], the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris.<ref name=WP>{{URLwikipedia|Clitoris|Clitoris|2021-11-24}}</ref><ref>{{REFbook | ||
|last=Goodman | |last=Goodman | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| + | [[File:Clitoris glans - detailed.jpg|thumb|Location of (1) [[clitoral hood]] and (2) [[clitoral glans]]]] | ||
The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure.<ref>{{REFbook | The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure.<ref>{{REFbook | ||
|last=Rodgers | |last=Rodgers | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
|first2=Dana S. | |first2=Dana S. | ||
|last3=Hammer | |last3=Hammer | ||
| − | | | + | |first3=Elizabeth Yost |
|year=2011 | |year=2011 | ||
|title=Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century | |title=Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century | ||
Revision as of 08:43, 24 November 2021
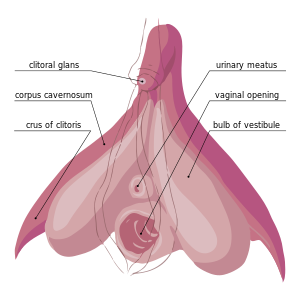
The clitoris is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris.[1][2][3][4]
The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure.[5][6][7][8][9] In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the embryo called the genital tubercle. Initially undifferentiated, the tubercle develops into either a penis or a clitoris during the development of the reproductive system depending on exposure to androgens (which are primarily male hormones). The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The glans (head) of the human clitoris is roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have about 8,000 sensory nerve endings.[1][9]
References
- ↑ a b
 Wikipedia article: Clitoris. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
Wikipedia article: Clitoris. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ↑
 Goodman, S. (2009):
Goodman, S. (2009): Family Eupleridae (Madagascar Carnivores)
, in: Handbook of the Mammals of the World. 1: Carnivores. Wilson, D.; Mittermeier, R. (eds.). Lynx Edicions. ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1. - ↑
 Roughgarden, Joan: Evolution's Rainbow: Diversity, Gender, and Sexuality in Nature and People. University of California Press. Pp. 37-40. ISBN 978-0-520-24073-5.
Roughgarden, Joan: Evolution's Rainbow: Diversity, Gender, and Sexuality in Nature and People. University of California Press. Pp. 37-40. ISBN 978-0-520-24073-5.
- ↑
 Wingfield, John C.:
Wingfield, John C.: Communicative Behaviors Hormone–Behavior Interactions, and Reproduction in Vertebrates
, in: Physiology of Reproduction. Neill, Jimmy D. (ed.). Edition: 2. Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 978-0-12-515402-4. - ↑
 Rodgers, Joann Ellison (2003): Sex: A Natural History. Macmillan. Pp. 92-93. ISBN 978-0805072815.
Rodgers, Joann Ellison (2003): Sex: A Natural History. Macmillan. Pp. 92-93. ISBN 978-0805072815.
- ↑
 O'Connell HE, Sanjeevan KV, Hutson JM. Anatomy of the clitoris. The Journal of Urology. October 2005; 174(4): 1189–95. PMID. DOI.
O'Connell HE, Sanjeevan KV, Hutson JM. Anatomy of the clitoris. The Journal of Urology. October 2005; 174(4): 1189–95. PMID. DOI.
- ↑
 Greenberg, Jerrold S., Bruess, Clint E., Conklin, Sarah C (2010): Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Learning. P. 95. ISBN 978-0-7637-7660-2.
Greenberg, Jerrold S., Bruess, Clint E., Conklin, Sarah C (2010): Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Learning. P. 95. ISBN 978-0-7637-7660-2.
- ↑
 Weiten, Wayne, Dunn, Dana S., Hammer, Elizabeth Yost (2011): Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century. Cengage Learning. P. 386. ISBN 978-1-111-18663-0.
Weiten, Wayne, Dunn, Dana S., Hammer, Elizabeth Yost (2011): Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century. Cengage Learning. P. 386. ISBN 978-1-111-18663-0.
- ↑ a b
 Carroll, Janell L. (2012): Sexuality Now: Embracing Diversity. Cengage Learning. Pp. 110–111, 252. ISBN 978-1-111-83581-1.
Carroll, Janell L. (2012): Sexuality Now: Embracing Diversity. Cengage Learning. Pp. 110–111, 252. ISBN 978-1-111-83581-1.
