Difference between revisions of "Erection"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
WikiModEn2 (talk | contribs) m (→Side views and comparison of the stages human penis erection: typo.) |
WikiModEn2 (talk | contribs) (Add video section.) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
# the condition of becoming rigid and elevated, as erectile tissue when filled with blood. | # the condition of becoming rigid and elevated, as erectile tissue when filled with blood. | ||
| − | # especially the swelling and rigidity that occur in the [[Corpus cavernosum penis|two corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum]] of the [[penis]] as a result of sexual or other types of stimulation. Impulses received by the nervous system stimulate a flow of blood from the arteries leading to the penis, where the erectile tissue fills with blood, and the penis becomes firm and erect. Erection makes possible the transmission of semen into the body of the female. Erection can also occur to some extent in the [[clitoris]] and the nipples of the female.<ref>{{REFweb | + | # especially the swelling and rigidity that occur in the [[Corpus cavernosum penis|two corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum]] of the [[penis]] as a result of sexual or other types of stimulation. Impulses received by the nervous system stimulate a flow of blood from the arteries leading to the [[penis]], where the erectile tissue fills with blood, and the penis becomes firm and erect. Erection makes possible the transmission of [[semen]] into the body of the female. Erection can also occur to some extent in the [[clitoris]] and the nipples of the female.<ref>{{REFweb |
|url=https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/erection | |url=https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/erection | ||
|title=Erection | |title=Erection | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | [[Circumcised]] males may experience tight and/or painful erections if there is insufficient residual shaft [[skin]] to permit full expansion and extension of the shaft during erection. [[Tissue expansion]] may relieve the pain and tightness. | + | [[Circumcised]] males may experience tight and/or painful erections if there is insufficient residual shaft [[skin]] to permit full expansion and extension of the shaft of the [[penis]] during erection. [[Tissue expansion]] may relieve the pain and tightness. |
| + | == Video== | ||
| + | === How does an erection occur in men ? === | ||
| + | <youtube>v=52vH6gDUVI8</youtube> | ||
| + | {{REF}} | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[Category:Medical term]] | ||
[[Category:Male sexuality]] | [[Category:Male sexuality]] | ||
[[Category:Physiology]] | [[Category:Physiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:18, 27 April 2024
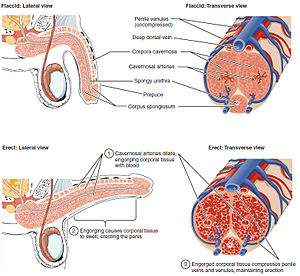
Erection is defined as:
- the condition of becoming rigid and elevated, as erectile tissue when filled with blood.
- especially the swelling and rigidity that occur in the two corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum of the penis as a result of sexual or other types of stimulation. Impulses received by the nervous system stimulate a flow of blood from the arteries leading to the penis, where the erectile tissue fills with blood, and the penis becomes firm and erect. Erection makes possible the transmission of semen into the body of the female. Erection can also occur to some extent in the clitoris and the nipples of the female.[1]
Contents
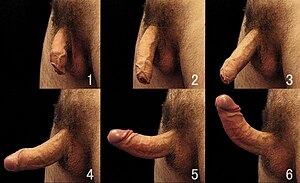
Side views and comparison of the stages human penis erection
Circumcised males may experience tight and/or painful erections if there is insufficient residual shaft skin to permit full expansion and extension of the shaft of the penis during erection. Tissue expansion may relieve the pain and tightness.