Difference between revisions of "Shock"
m (added File:CircShock Cuddles.jpg) |
WikiModEn2 (talk | contribs) (→"Felt nothing": Wikify.) |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Shock''' is one of the possible consequences of [[circumcision]], especially in newborns and infants at an age when effective pain suppression with general anesthesia is not possible. | + | [[File:PureShock.jpg|thumb|Baby in shock after circumcision]] |
| + | '''Shock''' is one of the possible consequences of [[circumcision]], especially in newborns and infants at an age when effective [[pain]] suppression with general anesthesia is not possible.<ref name="agoglu2022">{{REFjournal | ||
| + | |last=Aydoğlu | ||
| + | |first= | ||
| + | |init=B | ||
| + | |author-link= | ||
| + | |last2=Aydoğlu | ||
| + | |first2= | ||
| + | |init2=M | ||
| + | |author2-link= | ||
| + | |last3=Okur | ||
| + | |first3= | ||
| + | |init3=MH | ||
| + | |author3-link= | ||
| + | |etal=no | ||
| + | |title=Social and psychological effects of circumcision: A narrative review | ||
| + | |trans-title= | ||
| + | |language= | ||
| + | |journal=Journal of Applied Nursing and Health | ||
| + | |location= | ||
| + | |date=2022-12 | ||
| + | |volume=4 | ||
| + | |issue=2 | ||
| + | |pages=264-71 | ||
| + | |url=https://janh.candle.or.id/index.php/janh/article/view/110/138 | ||
| + | |archived= | ||
| + | |quote= | ||
| + | ||DOI=10.55018/janh.v4i2.110 | ||
| + | |format=PDF | ||
| + | |accessdate=2023-05-03 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
{{WikipediaQuote|URL=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shock_(circulatory)}} | {{WikipediaQuote|URL=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shock_(circulatory)}} | ||
<blockquote>Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. | <blockquote>Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. | ||
| − | Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: low volume, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Low volume shock, also known as hypovolemic shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting.[1] Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses.</blockquote> | + | Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: low volume, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Low volume shock, also known as hypovolemic shock, may be from [[bleeding]], diarrhea, or vomiting.[1] Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses.</blockquote> |
| − | + | The American Academy of Pediatrics advised: | |
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | When pain is prolonged, striking changes occur in the infant's physiologic and behavioral indicators. During episodes of prolonged pain, neonates enter a state of passivity with few, if any, body movements; an expressionless face; decreased heart rate and respiratory variability; and decreased oxygen consumption, all suggestive of a marked conservation of energy.<ref name="aap2016">{{REFjournal | ||
| + | |last= Committee on Fetus and Newborn and Section on Surgery; Section on Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine; | ||
| + | Canadian Paediatric Society; Fetus and Newborn Committee | ||
| + | |etal=no | ||
| + | |title=Prevention and Management of Pain in the Neonate: An Update | ||
| + | |trans-title= | ||
| + | |language= | ||
| + | |journal=Pediatrics | ||
| + | |location= | ||
| + | |date=2006-11 | ||
| + | |volume=118 | ||
| + | |issue=5 | ||
| + | |article= | ||
| + | |page= | ||
| + | |pages=2231–41 | ||
| + | |url=https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/118/5/2231/69964/Prevention-and-Management-of-Pain-in-the-Neonate?autologincheck=redirected | ||
| + | |archived= | ||
| + | |quote= | ||
| + | |pubmedID=17079598 | ||
| + | |pubmedCID= | ||
| + | |DOI=10.1542/peds.2006-2277 | ||
| + | |accessdate=2023-04-29 | ||
| + | }}</ref> <ref name="agoglu2022" /> | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
=== Neurogenic shock === | === Neurogenic shock === | ||
| + | [[File:AmericanBabyInShockAfterCircumcision.jpg|thumb|American baby in shock after circumcision]] | ||
In neurogenic shock, a nervous failure of the regulation of circulatory and / or vascular tone results in circulatory failure. Common causes of neurogenic shock are lesions of the spinal cord, spinal anesthesia and injuries or intoxication of the central nervous system (e.g. traumatic brain injury in a traffic accident). Cancer, meningitis and brain inflammation (encephalitis) are also among the causes of neurogenic shock. '''Functional neurogenic shock is less common, for example in the case of very strong pain stimuli.'''<ref>{{REFweb | In neurogenic shock, a nervous failure of the regulation of circulatory and / or vascular tone results in circulatory failure. Common causes of neurogenic shock are lesions of the spinal cord, spinal anesthesia and injuries or intoxication of the central nervous system (e.g. traumatic brain injury in a traffic accident). Cancer, meningitis and brain inflammation (encephalitis) are also among the causes of neurogenic shock. '''Functional neurogenic shock is less common, for example in the case of very strong pain stimuli.'''<ref>{{REFweb | ||
|url=https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schock_(Medizin)#Neurogener_Schock | |url=https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schock_(Medizin)#Neurogener_Schock | ||
| Line 13: | Line 69: | ||
|accessdate=2020-12-20 | |accessdate=2020-12-20 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| − | |||
== Hypovolemic shock == | == Hypovolemic shock == | ||
Every operation, including [[circumcision]], can lead to severe blood loss, which can lead to a “traumatic-hemorrhagic shock” (bleeding as a result of traumatic effects). | Every operation, including [[circumcision]], can lead to severe blood loss, which can lead to a “traumatic-hemorrhagic shock” (bleeding as a result of traumatic effects). | ||
| Line 25: | Line 80: | ||
=== Traumatic hemorrhagic shock === | === Traumatic hemorrhagic shock === | ||
| − | The early complications of circumcision are bleeding, pain, inadequate skin removal, and surgical site infection, but they usually tend to be minor. Of these, bleeding is the most common complication of circumcision. Bleeding may occur along the skin edges between sutures or from a discrete blood vessel, most commonly at the frenulum.<ref>{{REFjournal | + | The early complications of circumcision are [[bleeding]], [[pain]], inadequate [[skin]] removal, and surgical site [[infection]], but they usually tend to be minor. Of these, bleeding is the most common complication of circumcision. Bleeding may occur along the [[skin]] edges between sutures or from a discrete blood vessel, most commonly at the [[frenulum]].<ref>{{REFjournal |
|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4005087/ | |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4005087/ | ||
|title=Hypovolemic Shock after Circumcision | |title=Hypovolemic Shock after Circumcision | ||
| Line 58: | Line 113: | ||
File:CircShock Stared.jpg | File:CircShock Stared.jpg | ||
File:CircShock Cuddles.jpg | File:CircShock Cuddles.jpg | ||
| + | File:CircShock Traumatized.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 120: | ||
* [https://alphamom.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/05/wonderland_circumcision-e1273195287922.jpg alphamom.com: Circumcision: the kindest cut, or the cruelest?] | * [https://alphamom.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/05/wonderland_circumcision-e1273195287922.jpg alphamom.com: Circumcision: the kindest cut, or the cruelest?] | ||
| − | Infants regularly go into shock during circumcision due to the extreme pain they cannot escape and from which they cannot defend themselves (because of being restrained by a [[Circumstraint]] or because of being held by adults). This is their only way to turn off pain perception. Visible symptoms are usually very swollen eyelids and puffy faces after the intense screaming before. With some, the apathetic eyes do not close by themselves in shock. | + | Infants regularly go into shock during [[circumcision]] due to the extreme [[pain]] they cannot escape and from which they cannot defend themselves (because of being restrained by a [[Circumstraint]] or because of being held by adults).<ref name="agoglu2022" /> This is their only way to turn off pain perception. Visible symptoms are usually very swollen eyelids and puffy faces after the intense screaming before. With some, the apathetic eyes do not close by themselves in shock. |
=== "Felt nothing" === | === "Felt nothing" === | ||
[[File:Britmila2.jpg|thumb|infant after [[Brit Milah]]]] | [[File:Britmila2.jpg|thumb|infant after [[Brit Milah]]]] | ||
| − | Parents are very often misled by the statement by doctors and nurses that the child did not feel anything and is now sleeping peacefully. Often the parents are not present at the circumcision either. Newborns do not yet have any or only very few blockers of the nociceptors that transmit pain sensations to the brain. | + | Parents are very often misled by the statement by doctors and nurses that the child did not feel anything and is now sleeping peacefully. Often the parents are not present at the circumcision either. Newborns do not yet have any or only very few blockers of the nociceptors that transmit [[pain]] sensations to the brain. |
| − | When circumcision techniques last several minutes, children often go into a freeze, which was previously misinterpreted as falling asleep peacefully and which led to the belief that babies felt no pain. Measurements in such cases resulted in an usually 3 to 4 times increased cortisol value, which corresponds to a severe [[shock]] state.<ref>{{REFjournal | + | When circumcision techniques last several minutes, children often go into a freeze, which was previously misinterpreted as falling asleep peacefully and which led to the belief that babies felt no [[pain]]. Measurements in such cases resulted in an usually 3 to 4 times increased cortisol value, which corresponds to a severe [[shock]] state.<ref>{{REFjournal |
|last=Gunnar | |last=Gunnar | ||
|init=MR | |init=MR | ||
| Line 80: | Line 136: | ||
|init4=JM | |init4=JM | ||
|title=The effects of circumcision on serum cortisol and behavior | |title=The effects of circumcision on serum cortisol and behavior | ||
| − | |url= | + | |url=http://www.cirp.org/library/pain/gunnar/ |
|journal=Psychoneuroendocrinology | |journal=Psychoneuroendocrinology | ||
|date=1981 | |date=1981 | ||
| Line 91: | Line 147: | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| − | We owe the perception of pain to so-called nociceptors, free nerve endings that are excited when the body is injured or damaged. These specialized nerve cells are distributed all over the body; they send their signals via the spinal cord to the brain, where the excitation is then processed and interpreted as pain. The number of nociceptors exceeds that of all other receptors and their reporting system is largely independent of other sensory channels such as the sensation of warmth or touch. This shows how central the perception of pain is for the organism.<ref>{{REFweb | + | We owe the perception of [[pain]] to so-called nociceptors, free nerve endings that are excited when the body is injured or damaged. These specialized nerve cells are distributed all over the body; they send their signals via the spinal cord to the brain, where the excitation is then processed and interpreted as [[pain]]. The number of nociceptors exceeds that of all other receptors and their reporting system is largely independent of other sensory channels such as the sensation of warmth or touch. This shows how central the perception of pain is for the organism.<ref>{{REFweb |
|url=https://www.dasgehirn.info/wahrnehmen/fuehlen/schmerzlich-aber-unabdingbar | |url=https://www.dasgehirn.info/wahrnehmen/fuehlen/schmerzlich-aber-unabdingbar | ||
|title=Schmerzlich, aber unabdingbar | |title=Schmerzlich, aber unabdingbar | ||
| Line 100: | Line 156: | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| − | The facial expressions of these children are described by some [[intactivists]] as after being subjected to cruel torture (e.g. rape). Many babies are apathetic, no longer respond to their parents' speech and have massive breastfeeding confusion. | + | The facial expressions of these children are described by some [[intactivists]] as after being subjected to cruel torture (e.g. rape). Many babies are apathetic, no longer respond to their parents' speech and have massive [[breastfeeding]] confusion. |
| + | |||
| + | Harvard [[trauma]] expert [[Bessel van der Kolk]], {{MD}}, explains: | ||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | "When fighting or running does not take care of the threat, we activate the last resort—the reptilian brain, the ultimate emergency system. This system is most likely to engage when we are physically immobilized, as when we are pinned down by an attacker or when a child has no escape from a terrifying caregiver. … Once this system takes over, other people, and we ourselves, cease to matter. Awareness is shut down and we may no longer even register physical pain."<ref name="vanderkolk2014">{{REFbook | ||
| + | |last=van der Kolk | ||
| + | |first=Bessel | ||
| + | |init=BA | ||
| + | |author-link=Bessel van der Kolk | ||
| + | |year=2014 | ||
| + | |title=The Body Keeps the Score | ||
| + | |url= | ||
| + | |page=85 | ||
| + | |isbn=978-0-14-312774-1 | ||
| + | |accessdate=2021-08-10 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
=== Witch sleep === | === Witch sleep === | ||
| Line 117: | Line 189: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | {{SEEALSO}} | ||
| + | * [[Breastfeeding]] | ||
| + | * [[Circumcision industry]] | ||
| + | * [[Circumstraint]] | ||
| + | * [[Pain]] | ||
| + | * [[Trauma]] | ||
| + | {{LINKS}} | ||
| + | * {{REFdocument | ||
| + | |title=Child Genital Cutting as an Adverse Childhood Experience | ||
| + | |trans-title= | ||
| + | |language=English | ||
| + | |url=http://adversechildhoodexperiences.net/CGC_as_an_ACE.pdf | ||
| + | |archived= | ||
| + | |contribution= | ||
| + | |quote= | ||
| + | |trans-quote= | ||
| + | |quote-lang= | ||
| + | |last=Bollinger | ||
| + | |first=Dan | ||
| + | |author-link=Dan Bollinger | ||
| + | |last2=Chapin | ||
| + | |first2=Georganne | ||
| + | |author2-link=Georganne Chapin | ||
| + | |publisher=Intact America | ||
| + | |location=Tarrytown, New York, USA | ||
| + | |format=PDF | ||
| + | |date=2019-08-01 | ||
| + | |accessdate=2021-06-30 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{ABBR}} | ||
{{REF}} | {{REF}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Circumcision risk]] | [[Category:Circumcision risk]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Breastfeeding]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pain]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Parental information]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Trauma]] | ||
[[de:Schock]] | [[de:Schock]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:04, 17 August 2024
Shock is one of the possible consequences of circumcision, especially in newborns and infants at an age when effective pain suppression with general anesthesia is not possible.[1]
(The following text or part of it is quoted from the free Wikipedia:)
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: low volume, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Low volume shock, also known as hypovolemic shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting.[1] Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses.
The American Academy of Pediatrics advised:
When pain is prolonged, striking changes occur in the infant's physiologic and behavioral indicators. During episodes of prolonged pain, neonates enter a state of passivity with few, if any, body movements; an expressionless face; decreased heart rate and respiratory variability; and decreased oxygen consumption, all suggestive of a marked conservation of energy.[2] [1]
Contents
Neurogenic shock
In neurogenic shock, a nervous failure of the regulation of circulatory and / or vascular tone results in circulatory failure. Common causes of neurogenic shock are lesions of the spinal cord, spinal anesthesia and injuries or intoxication of the central nervous system (e.g. traumatic brain injury in a traffic accident). Cancer, meningitis and brain inflammation (encephalitis) are also among the causes of neurogenic shock. Functional neurogenic shock is less common, for example in the case of very strong pain stimuli.[3]
Hypovolemic shock
Every operation, including circumcision, can lead to severe blood loss, which can lead to a “traumatic-hemorrhagic shock” (bleeding as a result of traumatic effects).
Hypovolemic shock or volume depletion shock is a form of shock that results from a decrease in the amount of blood circulating, e.g. after major blood or plasma losses, severe vomiting, as well as pronounced diarrhea or severe burns.[4]
Traumatic hemorrhagic shock
The early complications of circumcision are bleeding, pain, inadequate skin removal, and surgical site infection, but they usually tend to be minor. Of these, bleeding is the most common complication of circumcision. Bleeding may occur along the skin edges between sutures or from a discrete blood vessel, most commonly at the frenulum.[5]
The primary treatment for blood loss is hemostasis; further symptomatic therapy consists of balancing out the metabolic acidosis with bicarbonate buffer solution, preventing the occurrence of a shock kidney or a stress ulcer and, if necessary, treating shock-induced lung damage and blood clotting failure.[6]
Misinterpretation of the shock
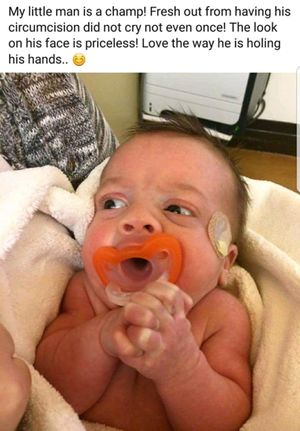
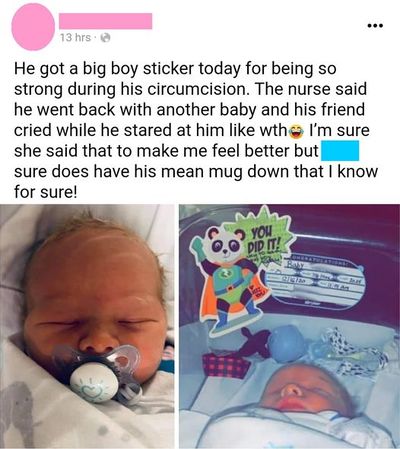
More and more parents (especially from the USA) are posting photos of their newborn sons on the Internet after genital mutilation. Your comments on the photos often testify to a complete misinterpretation of the situation.
- Example postings from social media
Other publicly visible photos of newborn boys in shock after circumcision:
- timesofisrael.com: Berlin declares circumcision legal, but only if performed by a doctor — not as a ritual
- alphamom.com: Circumcision: the kindest cut, or the cruelest?
Infants regularly go into shock during circumcision due to the extreme pain they cannot escape and from which they cannot defend themselves (because of being restrained by a Circumstraint or because of being held by adults).[1] This is their only way to turn off pain perception. Visible symptoms are usually very swollen eyelids and puffy faces after the intense screaming before. With some, the apathetic eyes do not close by themselves in shock.
"Felt nothing"
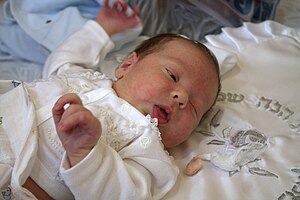
Parents are very often misled by the statement by doctors and nurses that the child did not feel anything and is now sleeping peacefully. Often the parents are not present at the circumcision either. Newborns do not yet have any or only very few blockers of the nociceptors that transmit pain sensations to the brain.
When circumcision techniques last several minutes, children often go into a freeze, which was previously misinterpreted as falling asleep peacefully and which led to the belief that babies felt no pain. Measurements in such cases resulted in an usually 3 to 4 times increased cortisol value, which corresponds to a severe shock state.[7]
We owe the perception of pain to so-called nociceptors, free nerve endings that are excited when the body is injured or damaged. These specialized nerve cells are distributed all over the body; they send their signals via the spinal cord to the brain, where the excitation is then processed and interpreted as pain. The number of nociceptors exceeds that of all other receptors and their reporting system is largely independent of other sensory channels such as the sensation of warmth or touch. This shows how central the perception of pain is for the organism.[8]
The facial expressions of these children are described by some intactivists as after being subjected to cruel torture (e.g. rape). Many babies are apathetic, no longer respond to their parents' speech and have massive breastfeeding confusion.
Harvard trauma expert Bessel van der Kolk, M.D.[a 1], explains:
"When fighting or running does not take care of the threat, we activate the last resort—the reptilian brain, the ultimate emergency system. This system is most likely to engage when we are physically immobilized, as when we are pinned down by an attacker or when a child has no escape from a terrifying caregiver. … Once this system takes over, other people, and we ourselves, cease to matter. Awareness is shut down and we may no longer even register physical pain."[9]
Witch sleep
An analogy to the misinterpretation of shock sleep in newborns after genital mutilation, which is still common today, can already be found in the Middle Ages in the so-called "witch sleep":
| “ | Kramer showed no mercy in this. He was particularly interested in women. They are particularly easy to be seduced by the devil. The author described exactly how witches are "exposed": with torture! The witch hunters then shaved the suspects all over their bodies, cut their nails to the flesh and tortured them in the worst possible way. If the victims fainted from pain, the torturers interpreted this as evidence of the "witch's sleep". Through him, they claimed, the devil protected his followers from agony. – Heinrich Kramer (1430–1505), Author of the so-called "Hexenhammer" (Witch Hammer) (GEOlino)[10] |
See also
External links
 Bollinger, Dan / Georganne Chapin: Child Genital Cutting as an Adverse Childhood Experience
Bollinger, Dan / Georganne Chapin: Child Genital Cutting as an Adverse Childhood Experience  , Intact America (Tarrytown, New York, USA). (1 August 2019). Retrieved 30 June 2021.
, Intact America (Tarrytown, New York, USA). (1 August 2019). Retrieved 30 June 2021.
Abbreviations
- ↑

Doctor of Medicine
, Wikipedia. Retrieved 14 June 2021. In the United Kingdom, Ireland and some Commonwealth countries, the abbreviation MD is common.
References
- ↑ a b c
 Aydoğlu B, Aydoğlu M, Okur MH. Social and psychological effects of circumcision: A narrative review
Aydoğlu B, Aydoğlu M, Okur MH. Social and psychological effects of circumcision: A narrative review  . Journal of Applied Nursing and Health. December 2022; 4(2): 264-71. DOI. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
. Journal of Applied Nursing and Health. December 2022; 4(2): 264-71. DOI. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ↑
 Committee on Fetus and Newborn and Section on Surgery; Section on Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine;
Canadian Paediatric Society; Fetus and Newborn Committee. Prevention and Management of Pain in the Neonate: An Update. Pediatrics. November 2006; 118(5): 2231–41. PMID. DOI. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
Committee on Fetus and Newborn and Section on Surgery; Section on Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine;
Canadian Paediatric Society; Fetus and Newborn Committee. Prevention and Management of Pain in the Neonate: An Update. Pediatrics. November 2006; 118(5): 2231–41. PMID. DOI. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ↑

Schock (Medizin) #Neurogener Schock
, Wikipedia. Retrieved 20 December 2020. - ↑

Hypovolämischer Schock
, DocCheck Flexikon. Retrieved 20 December 2020. - ↑
 Sarsu SB, Belen B. Hypovolemic Shock after Circumcision. APSP J Case Rep. 1 April 2014; 5(1): 13. PMID. PMC.
Sarsu SB, Belen B. Hypovolemic Shock after Circumcision. APSP J Case Rep. 1 April 2014; 5(1): 13. PMID. PMC.
- ↑

Schock (Medizin) #Hypovolämischer Schock
, Wikipedia. Retrieved 20 December 2020. - ↑
 Gunnar MR, Fisch RO, Korsvik S, Donhowe JM. The effects of circumcision on serum cortisol and behavior. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1981; 6(3): 269-75. PMID. DOI. Retrieved 20 December 2020.
Gunnar MR, Fisch RO, Korsvik S, Donhowe JM. The effects of circumcision on serum cortisol and behavior. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1981; 6(3): 269-75. PMID. DOI. Retrieved 20 December 2020.
- ↑
 Karberg, Sascha.
Karberg, Sascha. Schmerzlich, aber unabdingbar
, dasgehirn.info. Retrieved 20 December 2020. - ↑
 van der Kolk BA (2014): The Body Keeps the Score. P. 85. ISBN 978-0-14-312774-1. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
van der Kolk BA (2014): The Body Keeps the Score. P. 85. ISBN 978-0-14-312774-1. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ↑

Die Zeit der Hexenverfolgung
[The time of the witch hunt] (English). Retrieved 20 December 2020.